1996 PCED OBDI | SECTION 18: Diesel Diagnosis — 7.3L DI Engine |
The purpose of this test is to see if the fuel system is getting sufficient clean fuel to operate correctly.
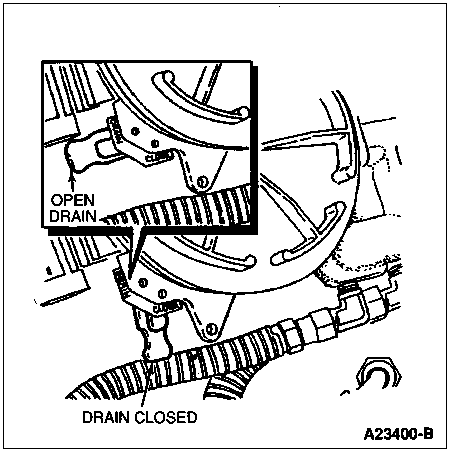
Route a hose from the fuel drain line to a clear container and open the drain. Idle the engine and observe the fuel flowing into the container. Shut the engine off when the container is half full.
Observe WATER IN FUEL lamp while cranking. If the lamp is illuminated the fuel is probably contaminated with water.
Flow out of the drain should be a steady stream. Insufficient flow could indicate fuel supply or fuel system problems.
Inspect fuel in the container, it should be straw colored but not cloudy. It also should be free of water and contaminants. Dyed red or blue fuel indicates off-highway fuel.
If engine oil is present in the fuel it may indicate an injector O-ring leak and subsequent loss of rail pressure. If that is suspected, check rail pressure during engine cranking (refer to Hard Start/No Start Diagnostic Procedures Step 9C).
Some sediment and water may be present in the fuel sample if the fuel filter has not been serviced for a prolonged period of time and/or if the sediment and water have not been drained recently. If that is the case a second sample may be required to determine fuel quality.
Cloudy fuel indicates that the fuel may not be a suitable grade for cold temperatures. Excessive water or contaminants may indicate that the tank and fuel system may need to be flushed and cleaned.
Clear container — approximately 1-quart
To determine if there is enough oil or oil of sufficient quality to operate the injectors.
Check oil level with oil level dipstick. If there is no oil or very little oil in the crankcase, the injectors will not operate.
If the oil level is overfull, it is possible the engine was incorrectly serviced or fuel is diluting the oil and filling the crankcase. If a substantial amount of fuel is in the oil, it will have a fuel odor.
Inspect oil for color. A milky white oil indicates possible coolant contamination which will have an ethylene glycol odor.
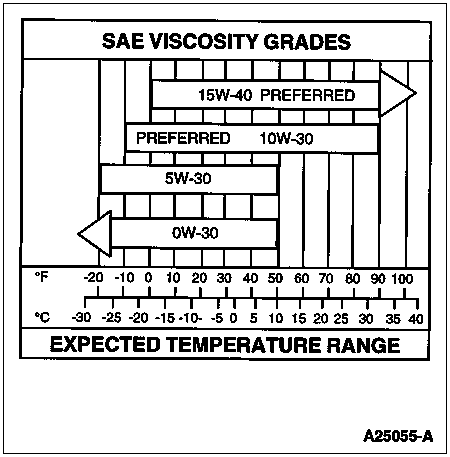
Check service records for correct oil type and viscosity for the vehicle operating temperature. Single weight or 15W-40 oil is not recommended for cold ambient temperatures. 10W-30 oil is recommended for cold ambient temperatures. Oil that has had extended drain intervals will have increased viscosity (become thicker) and will make engine cranking more difficult and starting less reliable at temperatures below freezing. Refer to the lube oil chart in the service manual or operator's manual for the correct oil selection for temperature conditions.
The level in the oil reservoir should also be checked. Remove the inspection plug in top of reservoir and check to see if the oil reservoir is full (a reservoir that drains back after the engine has not been operated for a period of time can cause a hard start or a start and die condition). Filling the reservoir will allow the system to prime faster, facilitating starting.
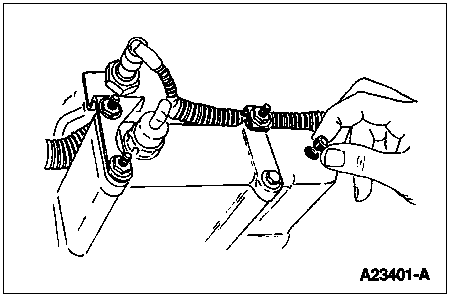
1/4-inch drive ratchet or breaker bar to remove inspection plug
This is a visual inspection to determine if an air intake restriction is contributing to a low power condition. If the engine does have a high air intake restriction, a considerable amount of black or blue smoke may be produced.
Inspect the air cleaner inlet and ducting to assure that it is not blocked or collapsed. Inspect the air cleaner housing and filter for proper installation.
If necessary, use Rotunda Pressure Adapter Kit 014-00761 or equivalent to install a Magnehelic® gauge on the port on the air cleaner and measure restriction at high idle.
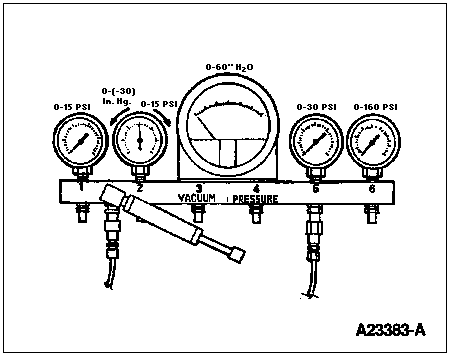
Magnehelic® gauge (part of Rotunda Pressure Adapter Kit 014-00761 or equivalent)
To determine if the PCM has detected any fault conditions that would cause a performance problem.

Connect the NGS Tester to the DLC under the dash. Turn off accessories. If vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary powertrain control (rpm control), it must be turned off to perform self tests.
If performing repeated self tests, it may be necessary to unplug glow plug relay to keep battery from going dead. Ignore DTC 0380 while glow plug relay is unplugged.
Note: If IDM trouble codes are retrieved, use the following special instructions required to clear IDM trouble codes (1995/1996 model year).
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent
To determine if the PCM has detected any historical or intermittent fault conditions that would cause a performance symptom. The condition that caused a continuous DTC may no longer exist.

Connect the NGS Tester to the DLC under the dash. Turn off accessories. If vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary powertrain control (rpm control), it must be turned off to perform self tests.
If performing repeated self tests, it may be necessary to unplug glow plug relay to keep battery from going dead. Ignore DTC 0380 while glow plug relay is unplugged.
Note: IDM codes must be cleared in this mode even though they only appear in KOEO On-Demand Self Test. If IDM trouble codes are retrieved, use the following special instructions required to clear IDM trouble codes (1995/1996 model year).
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent

Note: If unable to perform KOEO Injector Electrical Self Test, disconnect IDM connector and check injector high and low sides for shorts or opens.
To determine if the injector solenoids and valves are operating, by buzzing all injectors together and then buzzing each injector in numerical sequence (1 through 8).

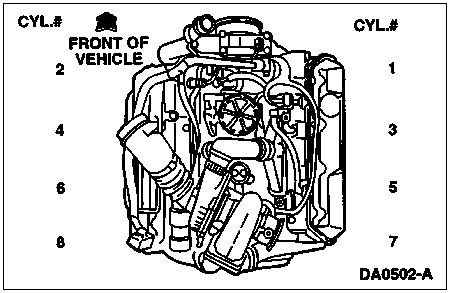
Note: If no DTCs are present and the KOEO Injector Electrical Self Test aborts while trying to perform, go to Pinpoint Test AB — Step AB29.
Connect the NGS Tester to the DLC under the dash. Turn off accessories. If vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary powertrain control (rpm control), it must be turned off to perform self tests.
If performing repeated self tests, it may be necessary to unplug glow plug relay to keep battery from going dead. Ignore DTC 0380 while glow plug relay is unplugged.
Note: If IDM trouble codes are retrieved, use the following special instructions required to clear IDM trouble codes (1995/1996 model year).
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent

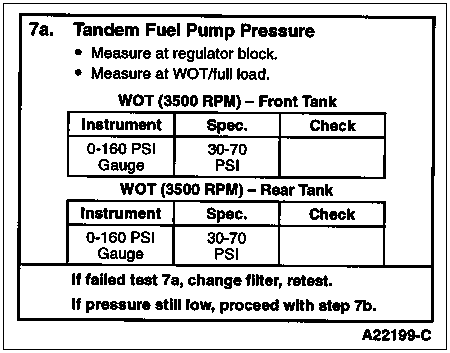
To determine if there is sufficient fuel pressure for correct engine operation.
Note if operator has indicated if the high fuel restriction lamp has been illuminated. A restricted fuel filter may be causing low fuel pressure.
Connect Rotunda High Fuel Pressure Adapter 014-00931-3 or equivalent to the Schrader valve mounted in the fuel regulator block on the side of the fuel filter housing. Connect a line for a 160 psi gauge to the adapter. Run the engine at low idle and check for leaks in the line to the gauge. Operate the engine at WOT (maximum engine speed out of gear with the brakes set and the wheels blocked). Measure maximum fuel pressure and compare to specification.
Repeat for front and rear tanks.
Change the fuel filter if the pressure is low and retest. If fuel pressure is still low, go to Performance Diagnostic Procedures Step 7b and check restriction from the fuel tank.
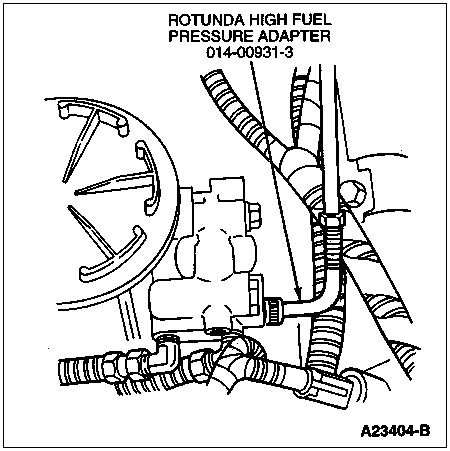
To determine if there is excessive restriction of fuel flow from the inlet fuel line to the fuel tank(s).
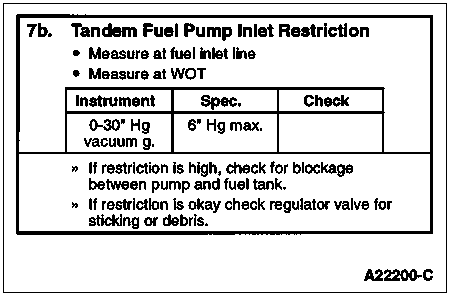
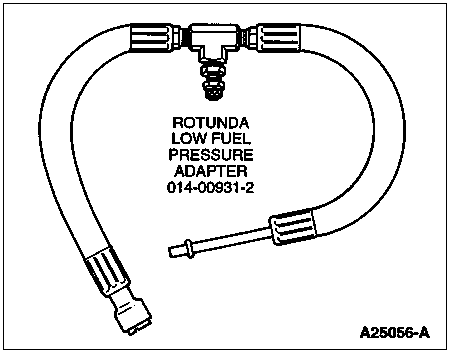
Remove the short rubber hose at the fuel inlet line (left side of engine close to the frame rail). The larger of the two fuel lines is the fuel inlet. The smaller line is fuel return. Install Rotunda Low Fuel Pressure Adapter 014-00931-2 or equivalent to the fuel inlet line and connect to a fuel restriction gauge (0 to 30 inch-Hg vacuum). Measure restriction at WOT (maximum engine speed out of gear with the brakes set and the wheels blocked). If restriction measures above specification, there is a blockage between the engine and the tank.

To determine if air is being drawn into the fuel system.
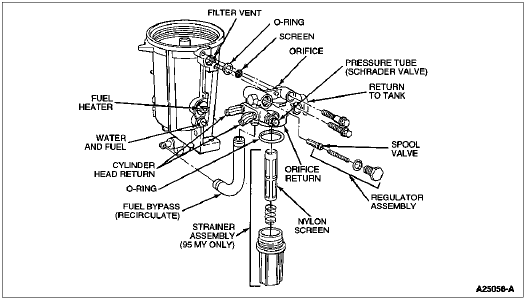
Note: If the filter has just been changed, air may be present in the clear line until purged from the system.
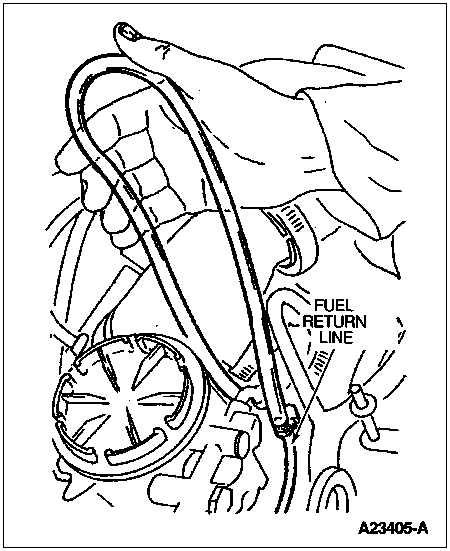
Loose and leaking fuel line fittings at:
Clear line and hose clamps
To determine if the PCM has detected any fault conditions that would cause a performance problem while the engine is running. This will perform step tests on the injection control pressure system and the exhaust back pressure system.
Step tests are PCM-controlled tests where the PCM commands a specific exhaust back pressure or injection control pressure and then measures the result. If a predetermined threshold is not reached, a fault code will be generated. This test can be performed at any engine temperature.
Connect the NGS Tester to the DLC under the dash. Turn off accessories. Turn A/C off. If vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary powertrain control (rpm control), it must be turned off to perform self tests.
Note: Engine will run rough during this test.
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent

To determine if the engine lube oil is aerated and causing poor idle quality.
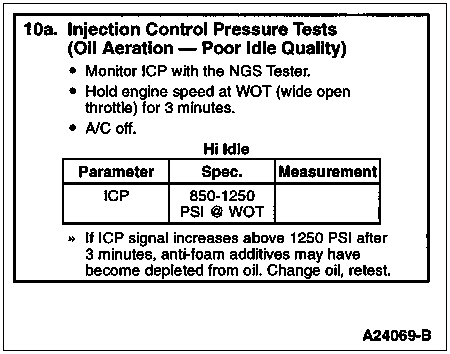
Install NGS Tester. Turn A/C off. Access ICP PID on NGS Tester and monitor ICP pressure. Operate the engine at wide open throttle for 3 minutes. This test should be performed with engine at normal operating temperature.
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent

To determine if idle stability and/or low power is caused by a stuck or dirty IPR or faulty ICP signal.
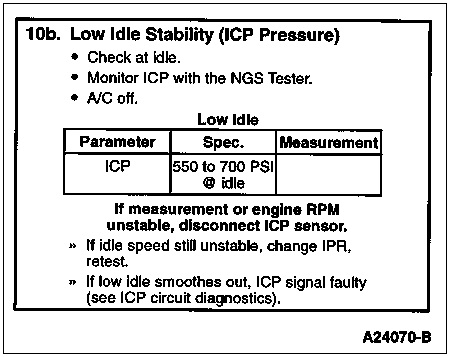
Install NGS Tester. Turn A/C off. Access ICP PID on NGS Tester and monitor ICP pressure. Operate the engine at low idle. If engine does not stabilize, disconnect the ICP sensor. If low idle speed stabilizes with the ICP sensor disconnected, the problem is most likely in the ICP sensor circuit. Refer to Pinpoint Test Z. If rpm does not stabilize, change the IPR and retest. This test should be performed with engine at normal operating temperature.
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent

This test will measure crankcase pressure. Crankcase pressure is a measure of how well the cylinders are sealing.
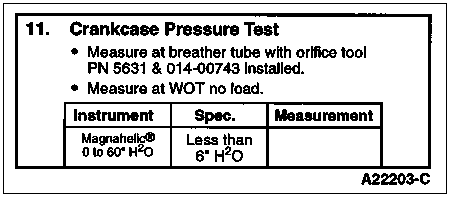
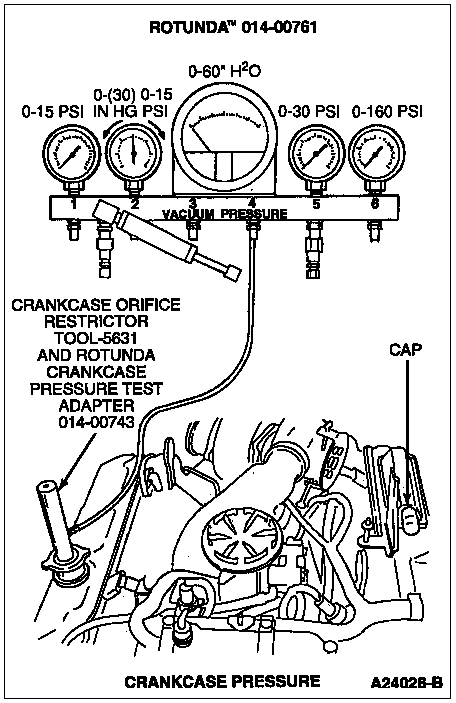
Note: Do not plug hole on Crankcase Orifice Restrictor Tool PN 5631.
Make sure the engine is up to operating temperature. A cold engine will give higher readings. Remove the ducting to the turbocharger inlet pipe and remove the inlet pipe and elbow that connects to the breather box. Block the outlet at the breather box with the cap provided in Rotunda Pressure Test Kit 014-00761 or equivalent. Install a protective screen over the turbocharger inlet.
Screw the Crankcase Orifice Restrictor Tool PN 5631 and Rotunda Crankcase Pressure Test Adapter 014-00743 or equivalent in the oil fill cap hole. Plumb to the Magnehelic® gauge in the gauge block. Make sure the Magnehelic® gauge has been zeroed.
Start the engine and operate at WOT. Hold for 30 seconds minimum and take a stabilized reading. Do not block the hole at the top of the restrictor tool.
Inspect air induction system. If the air induction system allows dirt to enter the cylinders, it will quickly "dust" the engine causing high crankcase pressure.
To test individual cylinders and injectors to determine if all are contributing equally to engine performance.
This is a test performed after a standard KOER test is performed.
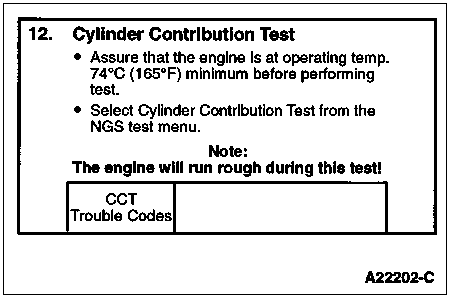
Note: Engine oil temperature must be above 74°C (165°F) or a fault code will be set.
Make sure engine is at operating temperature of 74°C (165°F). Turn A/C off. Install NGS Tester and select KOER Cylinder Contribution Self Test from NGS Tester menu. Engine will operate at an elevated low idle speed and run rough during this test.
Failing this test could indicate mechanical engine problems such as:
Refer to the service manual for base engine diagnostic procedures.
If the base engine condition meets specifications, the injector may not be functioning correctly and will need replacement. The solenoid and wiring should have been checked in earlier tests. Verify KOEO Injector Electrical Self Test passed.
Rotunda New Generation Star (NGS) Tester 007-00500 or equivalent

To determine if the exhaust system is sufficiently restricted to cause a performance problem.
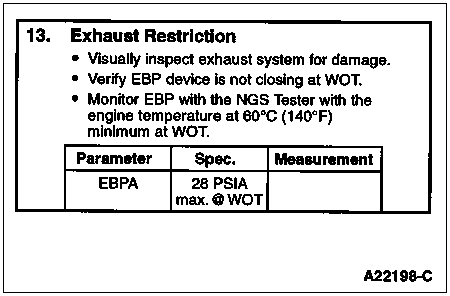
Use NGS Tester PID "EBPA." An "EBPA" reading above 28 psia indicates a restricted exhaust condition.
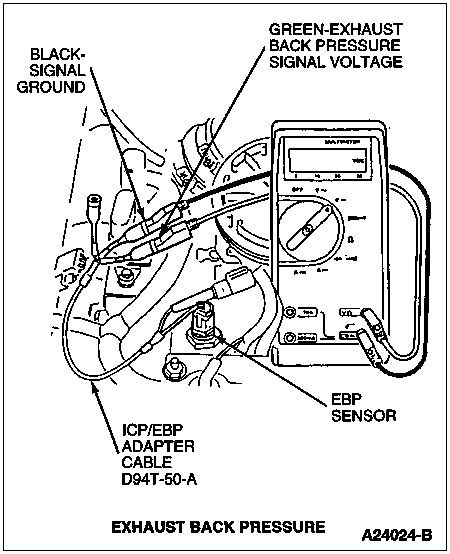
A thorough visual inspection will find the problem quickly in most instances. If an NGS Tester is not available and a measurement is necessary, measure voltage at exhaust back pressure (EBP) sensor using a DVOM and ICP/EBP Adapter Cable D94T-50-A. Measure this pressure at WOT, wheels blocked and brake engaged.

To determine if the engine can develop sufficient boost to obtain specific power.
If the engine can obtain specified boost there is no engine power problem. There may be chassis or applications concerns but the engine is performing as specified.
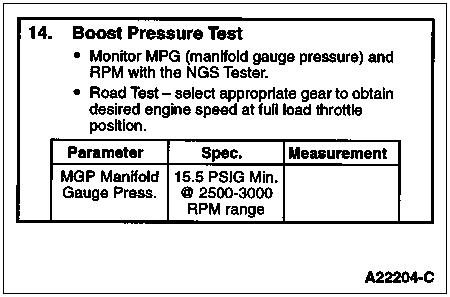
Monitor NGS PID "MGP." After the engine is up to operating temperature, find an open section of road and select the best gear to achieve a 2500 through 3000 rpm acceleration. With the accelerator at WOT, note the boost reading while accelerating through the 2500 to 3000 rpm range. Boost will level out after 3000 rpm. The highest boost reading will be noticed between 2500-3000 rpm.
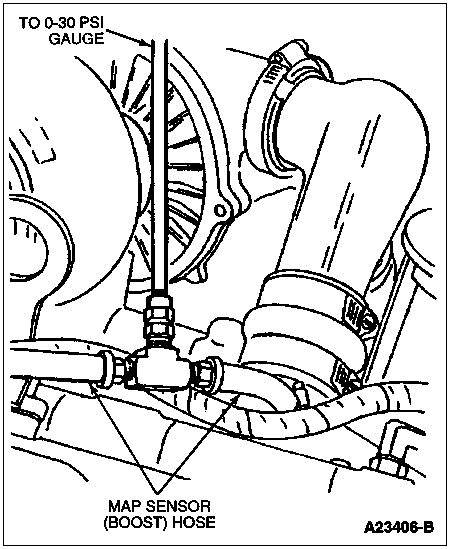
Install a "T" (manufactured locally out of common fittings) into the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor line that comes from the intake manifold. Make sure the MAP sensor is hooked up for this test.
Connect a "T" to a 0 to 30 psi gauge that is temporarily installed in the cab. Route the hose so that it is not crimped and does not come in contact with any hot surface.
After the engine is up to operating temperature find an open section of road and select the best gear to achieve a 2500 through 3000 rpm acceleration. With the accelerator at WOT, note the boost reading while accelerating through the 2500 to 3000 rpm range. Boost will level out after 3000 rpm. The highest boost reading will be noticed between 2500-3000 rpm. This test is best accomplished either climbing a hill or with the truck fully loaded.